Governance
Basic Policy
The Shimamura Group believes that the fundamental credibility of our business
comes from dealing fairly and equitably with various stakeholders.
Further enhancement of credibility and trust is necessary for sustained business growth and improvement in
corporate value over the medium- to long-term.
Therefore, the Shimamura Group will strengthen our governance system, enhance dialogue with shareholders and
investors, and implement thorough risk management.
1 Corporate governance
- Basic concept
-
The Shimamura Group believes that the basics of our business come from dealing fairly and equitably with various stakeholders such as employees, customers, business partners, shareholders, and society.
We recognize that further strengthening the confidence and trust from stakeholders surrounding our business is necessary for business continuity and growth. Furthermore, for that purpose, we recognize the importance of enhancing corporate governance.
Moreover, in order to further increase management efficiency and profitability by developing and expanding the unique business model that we have built in the retail industry, we believe that directors who possess highly-specialized business and operational knowledge should decide on financial and business policies at the Shimamura Group while complying with laws, regulations and the Articles of Incorporation, heighten corporate value and contribute to the common interests of all stakeholders.
2 Enhance dialogue with shareholders and investors
- Enhance dialogue with shareholders and investors
- From FY2020, in addition to the second quarter and year-end financial results briefings that had been
held thus far, the Shimamura Group began holding financial results briefings in the form of conference
calls for the first quarter and third quarter. We also began disclosing materials (with comments) for the
financial results briefings on our IR website. In FY2021, we will overhaul our corporate website to
enhance disclosure information. We will also strive to enhance financial results disclosure materials,
such as disclosure of Q&As at financial results briefings and expanded availability of
English-language materials.
In FY2024, we held briefing sessions (for analysts and institutional investors) for our growth businesses, Avail and Birthday. - IR coverage and dialogue at small meetings
- IR interviews are handled by the Corporate Planning Section, which is responsible for IR and corporate planning.In order to improve fairness and accuracy of our monthly disclosure, we changed our disclosure method in 2019 from individual telephone support to a conference call format (for sell-side analysts) which allows information to be sent to multiple people at the same time. We switched from a conference call format to a web conference format to improve convenience in FY2023. Additionally, our President will serve as speaker for small meetings that are held periodically. Other officers will also attend as necessary to support the meetings. We held a briefing session (for analysts and institutional investors) on Shimamura's business in FY2023. We shared information on product planning in the session.
- Disclosure of Medium-Term Management Plan
-
We have been disclosing our Long-Term Management Plan 2030 since FY2023 and our Medium-Term Management Plan 2027 since FY2024.
- IR policy enactment and disclosure
-
We appropriately provide capital market participants (e.g., shareholders, investors and analysts) and all other stakeholders with information on results, management policies and other areas associated with investment decisions with fairness, accuracy and continuity.
3 Compliance
Compliance Regulations
- Basic approach
- The Shimamura Group continues to engage in sincere corporate management to build long-term universal relationships of trust and confidence with various stakeholders including employees, customers, business partners, shareholders and society. The employees of the Shimamura Group comply with laws/regulations, internal rules and other regulations and then take responsible actions in accordance with social norms in line with this philosophy.
- Scope of application
- Employees, Directors, Audit & Supervisory Board Members, Executive Officers
- Organization and structure
-
-
Manager
- Each department head is responsible for confirming the status of compliance with laws/regulations, internal rules and other regulations as the compliance manager of the operations over which they have responsibility.
- The Legal Section is responsible for preventive legal activities for the prevention and mitigation of legal disputes, and strategic legal activities to perform legal work involving important decision-making in corporate management.
- Executive officers in charge of the General Administration Department and the Human Resources Department are responsible for overall compliance management.
-
Internal audit
The Audit Section conducts internal audit on the status of compliance with the internal rules to ensure the appropriateness of business operations. -
Whistleblowing system
We have set up a point of contact to accept inquiries and reports for organizational or personal violations of laws/regulations and Work Regulations.
-
Manager
-
-
Responsible product procurement and sales
The Shimamura Group thoroughly manage safety and comply with law and regulations on products, sales floors, advertising and other activities for our customers.
-
Respect for human rights
The Shimamura Group respects all human rights and does not tolerate discrimination, harassment or other forms of human rights violations.
To achieve that, we prevent human rights violations from occurring in advance. In the event a human rights violation does occur, we fulfill our responsibility to respect human rights as a company by taking the appropriate measures to correct that.
Moreover, we work with business partners to promote respect for human rights throughout our supply chain. -
Corruption prevention
The Shimamura Group does not engage in bribery, forgery, falsification or concealment of records, evidence or testimonies, and other unethical acts.
- We do not make any demands unrelated to product transactions to our business partners.
- We maintain sound and normal relationships with the government and authorities, and do not engage in bribes, illegal political contributions or other such acts.
- Employees do not take actions which harm the interests of the company for the benefits of themselves or a third party. They do not use the assets, information and other properties of the company for purposes other than business purposes.
-
Ensuring tax transparency
The Shimamura Group complies with laws and regulations applicable to the countries where we conduct our business activities. We appropriately file and pay taxes.
- We disclose management figures and our tax payment situation in a timely and appropriate manner in accordance with the laws and regulations applicable to the countries where we conduct our business activities.
- We appropriately communicate with the tax authorities and strive to build and maintain good relationships with them.
- We comply with the laws and regulations of each country, tax treaties and international taxation rules in international transactions.
- We do not avoid tax (not use tax havens).
-
Appropriate information disclosure
he Shimamura Group appropriately provides capital market participants (e.g., shareholders, investors and analysts) and all other stakeholders with information on results, management policies and other areas associated with investment decisions with fairness, accuracy and continuity.
-
Responsible information management
The Shimamura Group thoroughly protects personal and confidential information. We strictly manage them to avoid leaks.
Moreover, we do not use the information assets we possess for any purpose other than legitimate purposes. -
Prohibition of transactions with antisocial forces
When receiving unjust demands from antisocial forces, the Shimamura Group resolutely confronts such demands without resorting to easy solutions via payoffs.
We do not conduct any business with antisocial forces, or corporations and organizations thought to be related to antisocial forces. -
Protection of intellectual property
The Shimamura Group respects intellectual property rights and strives not to infringe the rights of other companies by conducting prior checks.
-
Social contribution
The Shimamura Group will strive for harmony with the local community and the international community, build friendly relationships with stakeholders, and actively contribute to the realization of a prosperous and comfortable society.
-
Environmental conservation
The Shimamura Group complies with laws and regulations relating to environmental conservation and conducts environmentally-friendly business activities.
We strive to prevent environmental pollution and to reduce our environmental burden by appropriately controlling the amount of energy and natural resources we use and treating waste, exhaust gas and wastewater.
In addition, we recognize the importance of biodiversity and strive to conserve it.
-
- Method of informing employees
-
We provide employee education on compliance to improve the effectiveness of these regulations.
Periodic training: We confirm the Compliance Regulations in ESG study sessions (all employees at least once a year).
Education for employees with a new position: New employee education (full-time employees)/new store manager education/education for employees assigned to a new department.
Departmental education: We provide specialized education by each department for matters necessary in operations. - Whistleblowing system
-
We have formulated the Regulations to Protect Whistleblowers. These regulations establish mechanisms for
proper handling of inquiries and reports from employees, etc. : full-time employees, regular employees
(part-timers), part-time employees, temporary employees, directors, auditors, executive officers,
employees who have been retired from the Company for less than one year, etc. in regards to organizational
(the Shimamura Group) or personal (employee) violations of laws, regulations, or Work Regulations. The
Company manages reports of legal violations as "Internal Whistleblowing" and reports Harassment of
violations of employment regulations, including harassment, as "Harassment Reporting.", which are
classified into two categories depending on the type of report.
-
Whistleblowing structure
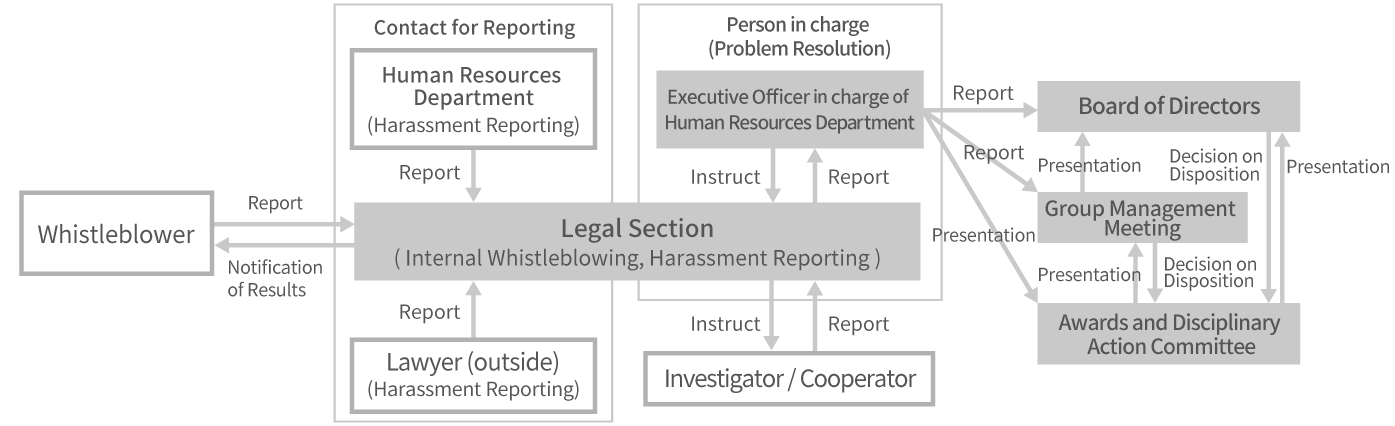
-
Person in charge of Whistleblowing
The executive officer in charge of the Human Resources Department develop and oversee a system to respond to internal whistleblowing. In addition, he reports to the Management Meeting or the Board of Directors, as appropriate, on the status of business execution in relation to the Whistleblower Protection Regulations.
The Legal Office is responsible for the development and proper operation of the system based on the Whistleblower Protection Regulations, as well as the education and dissemination of such regulations to employees and others under the direction of the executive officer in charge of the Human Resources Department. It also manages a series of operations from receipt, investigation, and correction of internal whistleblowing.
The auditor is responsible for investigating and correcting the matter in the case of internal whistleblower reports in which the company or a director or officer is the subject of the report.
-
Roles of the Board of Directors and the Group Management Committee
The executive officer in charge of the Human Resources Department reports all reported content, methods of addressing issues, and the results to the Management Committee or the Board of Directors, depending on the content. In addition, he presents a disciplinary action plan to the Awards and Disciplinary Action Committee. Then, the Management Committee or the Board of Directors makes a determination according to the content. -
Protection of a person who makes a report
- ・We do not dismiss, demotion, adverse personnel actions, pay cuts, de facto harassment or otherwise disadvantageously treat those who have made reports or inquiries due to their reports or inquiries. In addition, we do not make any claim for damages against a whistleblower for any loss or damage caused by the whistleblower's report.
- ・We take appropriate action so that the working environment of those who make reports or inquiries will not worsen.
- ・We prohibit the search for whistleblowers, except in unavoidable circumstances such as when it is impossible to conduct a necessary investigation without identifying the whistleblower, and we discipline any employee who does so in accordance with the employment regulations.
- ・We remind the informant that he/she must not be treated disadvantageously, and we take disciplinary action against employees who do so in accordance with the employment regulations.
-
Method of informing employees
We describe the whistleblowing system in a manual that can be viewed by all employees. In addition, we explain it in new employee education for full-time employees, regular employees (part-timers), and part-time employees, and post reporting acceptance slips and materials (e.g., a point of contact for reporting, how to make a report and the response after report). -
Number of whistleblowing cases (Total of Internal Whistleblowing and Harassment Reporting)
(cases)
Fiscal Year 2020 2021 2022 2023 2024 In-House Contacts (Legal Section, Human Resources Department) 7 9 20 16 25 Outside Contact (lawyer) 4 6 7 3 4 Total 11 15 27 19 29
-
Whistleblowing structure
4 Internal control
- Basic approach
- We have established the Internal Control Regulations. The purpose is to be a sincere and faithful company to our stakeholders as well as to maintain an organizational structure to establish and continuously improve the internal control system as required by the Companies Act and the Financial Instruments and Exchange Act.
- Ensuring the Appropriateness of Operations (Companies Act)
- We have established and is operating a system to ensure that the execution of duties by directors, executive officers and employees complies with laws and regulations and the Articles of Incorporation.
- Ensuring the Reliability of Financial Reporting (Financial Instruments and Exchange Act)
-
We have established and are operating a system to realize the four purposes to ensure that financial
reporting is properly conducted in accordance with laws and regulations.
- (1) We will enhance the effectiveness and efficiency of business operations to achieve the purposes of business activities.
- (2) We ensure reliability in financial reporting.
- (3) We promote compliance with laws/regulations and other norms relating to business activities.
- (4) We acquire, use and dispose of assets under appropriate procedures and approval.
- Internal control system
-
- The Board of Directors determines and supervises basic internal control policies.
- President develops, operates and evaluates internal control based on the basic policy determined by the Board of Directors and makes reports on the results.
- Auditors monitor and verify the development and operational status of internal control from an independent standpoint.
- The Audit Section takes responsibility for the ongoing confirmation of the effectiveness of the development and operational status of internal control, and makes reports to the President. Together with this, it promotes improvements in response to instructions from the President.
- The Heads of the Accounting Department, the Human Resources Department, the General Administration Department, the Systems Department and the Public Relations Section and Corporate Planning Section, which are the internal control-related departments, develop and operate the related documents necessary to evaluate internal control in their own departments.
- All employees in each department comply with the internal control established by the company while executing their own operations.
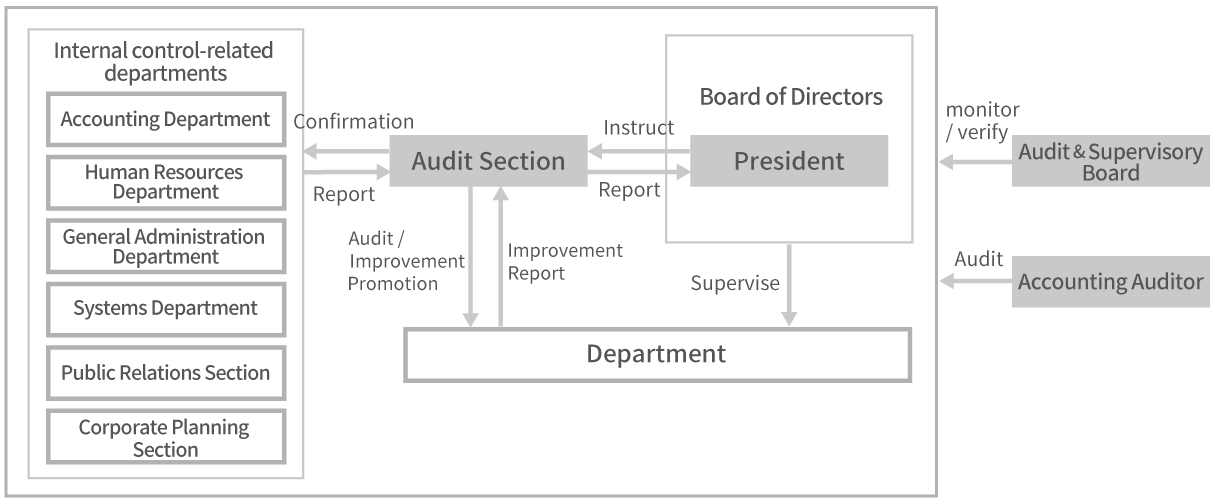
- Internal audit
-
-
Internal audit structure
We have established the Audit Section (five full-time members), which is an independent internal audit department under the direct control of the Representative Director,Chairman and Executive Officer. It periodically conducts on-site audits and evaluation of all stores, transfer centers and Head Office departments (targeted at department heads and those in senior class) at least once every 18 months in regards to the situation concerning compliance with internal rules, overall business activities and the validity of procedures. -
Results reporting
The Head of the Audit Section, the person in charge, makes weekly reports on the results of audits to the Representative Director,Chairman and Executive Officer and Full-time Audit & Supervisory Board members, thus constructing a dual reporting (two reporting channels) structure.
Moreover, the Head of the Audit Section reports the semi-annual reports to the Board of Directors twice a year and the annual results once a year to the Audit & Supervisory Board. -
PDCA cycle of internal audit
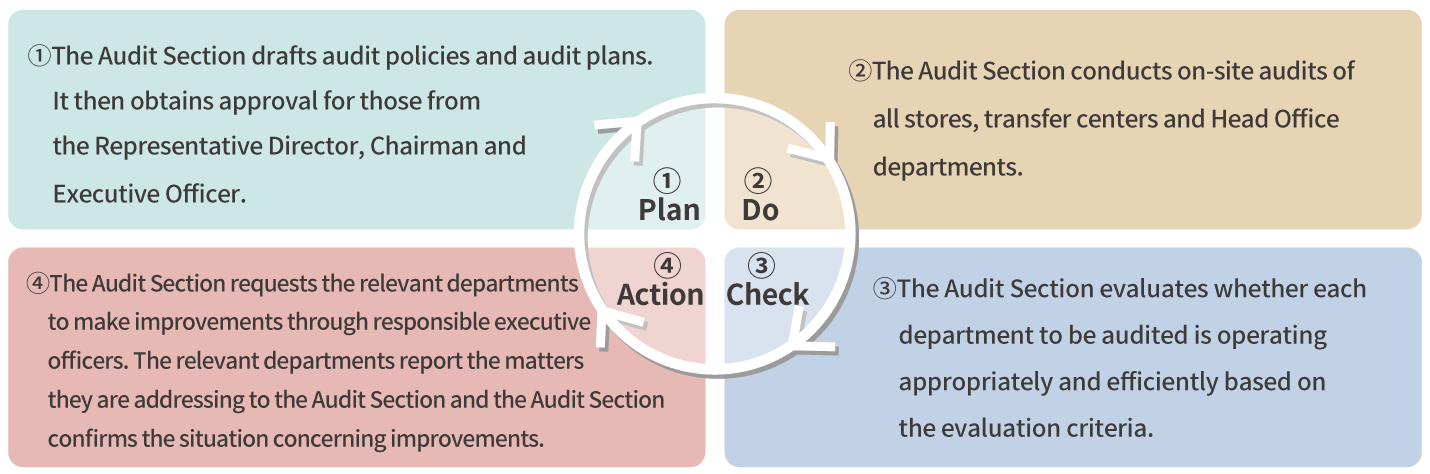
-
Internal audit structure
- Audit by auditors
- Auditors enhance the effectiveness of audits by attending meetings of the Board of Directors, meetings of the Management Committee and other important meetings to grasp important decision-making processes and the status of business execution. In addition, auditors conduct audits of the status of business execution by directors and executive officers. The Board of Auditors then verifies that.
5 Risk management
- Basic approach
-
- The Shimamura Group defines risk as "factors that hinder the achievement of goals" and classifies them broadly into the following three major categories:
"External environmental risks" such as climate change and changes in social conditions.
"Business activity risks" related to product procurement, logistics, etc.
"Management infrastructure risks" related to human capital and information management.
These risks are becoming increasingly diverse and complex. They may have a significant impact on our corporate activities depending on their nature. - Risk management refers to identifying risks which may become barriers in management in advance, classifying those risks according to the degree of impact they have on business activities, prioritizing them according to the risk level and then planning and implementing measures to prevent them. The aim of this risk management is to avoid risks or to minimize losses from them when they occur.
- The Shimamura Group considers risk management an important management issue. Accordingly, we work to prevent and reduce risks with the aim of increasing our corporate value through sustainable business activities and protecting human life and property.
- The Shimamura Group defines risk as "factors that hinder the achievement of goals" and classifies them broadly into the following three major categories:
- Guidelines for action
-
- We strive to identify risks and to prevent them to continue our business.
- If an incident occurs, we prioritize ensuring the safety of human life and then aim to conserve our business resources.
- If damages arise, we aim to take prompt action and to recover. We then strive to stably provide our products and services.
- We operate in a way in which we do not compromise the safety and interests of our stakeholders. In addition, we reflect social demands in our risk management.
- Our directors and executive officers take the lead in risk management and strive to improve the risk management capabilities of our employees.
- Division of duties and structural diagram in risk management
-
- Board of Directors
Board of Directors determines risk management regulations and basic risk management policies. They then develop a structure to be able to prevent risks and to respond appropriately in emergencies. The operational status of these regulations is assessed at least once a year. Instructions are given to executive officers and these regulations are reviewed according to the results of that assessment. - Group Management Director
Group management directors formulate measures against risk, and develop and operate a management structure for the departments in charge based on the basic policy determined by the Board of Directors. Moreover, they report to the Board of Directors and the Group Management Meeting about the status of risk management, new risks which have arisen and response to them. - Department head
Department heads appropriately manage risks in their own departments. - Public Relations Section
The Public Relations Section identifies, classifies and analyzes risks. They then compile measures designed by executive officers and report them to the Board of Directors. -
System Diagram

- Board of Directors
- Identification, classification, and analysis of risks
-
1.Identification and classification of risks
We analyze the external environment and internal environment surrounding the Shimamura Group. We identify what kind of risks exist now and what kind of risks will exist in the future. We divide risks we have identified into large categories, medium categories and small categories to lead to concrete measures against them. The following are the three main risks (large categories).- External environment risks
External environment risks include risks which affect not just our company but society as a whole such as climate change, disaster and infectious disease, geopolitical risks, market fluctuation, and information security. - Business activity risks
Business activity risks include risks which directly impact our business performance in performing our business activities such as store openings, product procurement, logistics and sales. - Management infrastructure risks
Management infrastructure risks include risks which impact the foundations of our management such as business strategies, human capital, ESG and information management/internal controls.
2. Risk analysis
In order to select priority given to our initiatives, we investigate the possibility of occurrence and analyze impacts on our management plan, and create the risk matrix.-
Possibility of occurrence
High Occurs intermittently or at several places every year Middle Occurs sporadically or once in several years Low Occurs once or once in dozens of years -
Impact on our management plan
Large High possibility of insufficient response or a failure to achieve plans when it occurs Medium Possibility of insufficient response or a failure to achieve plans when it occurs Small Insufficient response or impact is limited on our plans even if it occurs -
Risk matrix
We categorize risks from S, A, B, C to D with S having the highest possibility of occurrence and the most significant impact on our management plan.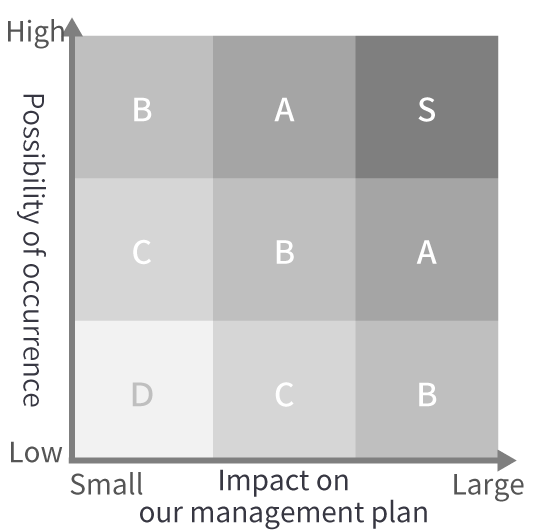
- External environment risks
- Main risks and countermeasures
-
Risk Main risk Countermeasures Identification and classification of risks ・Abnormal weather ・Implement product policies not affected by the weather, response for respective area and flexible sales promotions ・Natural disasters ・Review of BCP (Business Continuity Plan) ・Population decline/low birthrate and aging population in Japan ・Expand regional share by adding new product lines and relocation ・Political instability in producing countries and outbreaks of conflict around the world ・Diversification and decentralization of producing countries and suppliers ・Soaring prices for energy and raw materials ・Take energy-saving measures, expand purchases by the Import Department and review countries of production ・Rapid fluctuations in exchange rates such as an extremely weak yen ・Use foreign exchange contracts for purchases by the Import Department and stably produce products with fabric contracts and sewing line contracts ・Intentional threats such as cyber-attacks and unauthorized access ・Strengthen security and conduct BCP training External environment risks ・Insufficient new store openings ・Strengthening the opening of stores in urban areas and relocation of stores to the suburbs ・Decrease in existing stores due to the expiration of store contracts ・Maintain good relationships with existing store owners ・Increase in purchasing costs ・Expand high-priced products, expand purchases by the Import Department and review countries of production ・Delays in responding to changes in market needs ・Develop products using customer management systems and social networking site analysis tools ・Deterioration in product quality ・Improve awareness among suppliers and the Merchandise Department, and strengthen factory audits and product inspections by the Product Management Department ・Capacity increase in transfer centers ・Open new transfer centers and renovate existing transfer centers ・Increase in delivery costs ・Perform a modal shift in in-house logistics and utilize direct logistics ・Maintenance failures and deterioration of transfer centers ・Repair, renovate and relocate existing transfer centers ・Decline in labor productivity due to an increase in work ・Review routing work by promoting digital transformation Business activity risks ・Delays in changing business strategies and portfolios ・Research growth strategies for existing businesses and launch new businesses ・Damage to corporate image due to rumors and media reports ・Respond promptly through centralized information management and provide employee education ・Labor shortage ・Raise flexibility in employee recruitment and improve personnel and labor systems ・Personnel shortage ・Improve personnel and labor systems, enrich the education system, and respond to the promotion of female empowerment ・Delays in reforming work styles ・Review work structure ・Delays in training successors ・Enrich the education system, Implementing a successor training curriculum ・Decline in communication in organization ・Enrich the education system and utilize digital tools ・Delays in responding to environmental issues ・Promote recycling and reduce greenhouse gas emissions ・Delays in responding to social issues ・Give consideration to human rights in supply chains, reduce in-house harassment and promote diversity ・Delays in responding to governance issues ・Comply with and disclose the Corporate Governance Code ・Deterioration of system infrastructure ・Periodically replace equipment, store data on the cloud and strengthen security - Strengthen information security
-
The Shimamura Group recognizes that the protection and management of information assets are an important issue in risk management. Recognizing that, we have enacted the Information Security Regulations and Personal Information Protection Regulations and are working to strengthen information security.
Under these regulations, the Information Security Committee (Systems Department, General Administration Department, Public Relations Section and Audit Section, Legal Section) confirms the information security compliance situation, investigates and corrects problems, and provides education and information in order to minimize the impact from risks. The Information Security Committee is chaired by the executive officer responsible for the Systems Department. - Respond to risks during disasters and emergencies
-
-
BCP (Business Continuity Plan) development
The Shimamura Group recognizes that the Business Continuity are an important issue in risk management. Recognizing that, we have enacted BCP and are committed to responding to risks during disasters and emergencies.
In the event of a disaster, the President will announce the establishment of a Disaster Response Headquarters and appoint a Chief in charge of response by the Headquarters. Furthermore, if a disaster occurs, we will respond promptly based on the following items, and will support the disaster area and victims.
First, we will place top priority on protecting life.
Second, we will confirm and respond to the situation of damage to employees' homes, etc.
Third, we will protect the Company's assets and aim to quickly resume operations.
Fourth, we will create an environment for employees to quickly return to work.
Emergency responses to natural disasters, fires, customer injuries and illnesses, etc., during store operations are stipulated in the store operations manual. We educate and train our employees to place the highest priority on human life and safety. -
Systematization of safety confirmation
We have systematized the confirmation for employee safety during emergencies. This enables head office employees to use smartphones to confirm their safety, and store employees to use the intranet to confirm their safety and report on business conditions.
-
BCP (Business Continuity Plan) development
